Why a differential?
Article From:Changge Jingheng Machinery Manufacturing Co., LTD
The first thing to say is where the differential is installed, its position should be in the drive shaft and the left and right half shaft junction point, the power output from the gearbox is distributed to the left and right half shaft here. As for why the differential is installed, there is no need to explain more, Baidu Encyclopedia is very clear. We all know that the speed of the left and right driving wheels is the same when the car is driving in a straight line, but the distance between the two wheels is not equal in the turn, so the speed of the wheels will definitely be different. The function of the differential is to allow the left and right driving wheels to operate at different speeds.
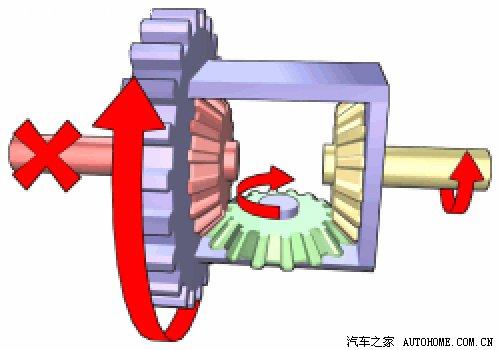
In fact, to put it bluntly, the core of the entire differential system is four gears: two planetary gears and two half-shaft gears connected to the drive shaft. All four gears are inside the differential housing, which is connected to the drive shaft and itself turns, turning in the same direction as the wheel when traveling.
We can explain the differential problem with a sphere! We assume that this sphere has two poles like the earth, and the line between the poles is autobiographical. This sphere can be understood as the differential housing, and the two poles of this housing are connected to the left and right axles of the car. Two half-shaft gears are installed here, and the connection between the center points of the two gears is the axis of rotation of the differential housing.
In addition to the two half-shaft gears, there are two planetary gears. Understanding the state of the two planetary gears is key to understanding the differential principle. Taking the sphere as an example, the two gears are mounted in opposite directions and perpendicular to the half-shaft gear, corresponding to the 6 o 'clock and 12 o 'clock positions. The two gears often rotate in opposite directions to achieve differential action. The shell rotates with two gears during its rotation.
Although these four gears are installed inside the housing, they can rotate independently of the differential housing, but they are interlocking with each other, and each side of each gear is interlocking with the other two gears (each half-shaft gear is interlocking with two planetary gears, each planetary gear is interlocking with two half-shaft gears). As long as one of the gears rotates, it will involve the other three gears to rotate together, and one of the gears rotates in a certain direction, and the opposite side of the gear must rotate in the opposite direction! This phenomenon can be verified by experiments: if both driving wheels of a car are suspended and one wheel is turned, the other wheel will turn in the opposite direction.
When driving in a straight line, the resistance of the left and right driving wheels is roughly the same. The power output from the engine is first transferred to the differential housing so that the differential housing begins to turn. Next to transfer the power from the housing to the left and right half shaft, we can understand that the two sides of the half shaft gear in the "struggle" with each other, because the two sides of the wheel resistance is the same, so neither of the two can break each other, so the differential housing in the planetary gear with the housing to rotate at the same time will not produce rotation, two planetary gears with the two half shaft gear to rotate at the same speed, So the car can go straight!
Suppose the vehicle is now turning left and the left drive wheel travels a short distance, relatively speaking, it will produce more resistance. The differential housing is connected through the gear and the output shaft, and the speed of the differential housing is also unchanged when the speed of the drive shaft is unchanged, so the left half shaft gear will turn slower than the differential housing, which is equivalent to the planetary gear driving the left half shaft will be more difficult, then the planetary gear will produce autobiography, transferring more torque to the right half shaft gear. Due to the revolution of the planetary gear plus its own autobiography, the right half shaft gear will increase on the basis of the speed of the differential housing, so that the right wheel will turn faster than the left wheel, so that the vehicle can achieve a smooth turn.
Impact of differential on off-road performance:
Because the differential allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds, on muddy roads, when a wheel slips, the power is all consumed in the rapidly rotating skid wheel, and the other wheels will lose power. In popular words, the differential is used to make the vehicle turn when the wheel has a wheel speed difference, otherwise the vehicle will be difficult to turn, but the differential is helpful on the off-road road.
Therefore, in the four-wheel drive vehicle, it is also necessary to have a device to limit and prevent slipping, such as differential lock, limited slip differential, traction control system, etc.
In fact, to put it bluntly, the core of the entire differential system is four gears: two planetary gears and two half-shaft gears connected to the drive shaft. All four gears are inside the differential housing, which is connected to the drive shaft and itself turns, turning in the same direction as the wheel when traveling.
We can explain the differential problem with a sphere! We assume that this sphere has two poles like the earth, and the line between the poles is autobiographical. This sphere can be understood as the differential housing, and the two poles of this housing are connected to the left and right axles of the car. Two half-shaft gears are installed here, and the connection between the center points of the two gears is the axis of rotation of the differential housing.
In addition to the two half-shaft gears, there are two planetary gears. Understanding the state of the two planetary gears is key to understanding the differential principle. Taking the sphere as an example, the two gears are mounted in opposite directions and perpendicular to the half-shaft gear, corresponding to the 6 o 'clock and 12 o 'clock positions. The two gears often rotate in opposite directions to achieve differential action. The shell rotates with two gears during its rotation.
Although these four gears are installed inside the housing, they can rotate independently of the differential housing, but they are interlocking with each other, and each side of each gear is interlocking with the other two gears (each half-shaft gear is interlocking with two planetary gears, each planetary gear is interlocking with two half-shaft gears). As long as one of the gears rotates, it will involve the other three gears to rotate together, and one of the gears rotates in a certain direction, and the opposite side of the gear must rotate in the opposite direction! This phenomenon can be verified by experiments: if both driving wheels of a car are suspended and one wheel is turned, the other wheel will turn in the opposite direction.
When driving in a straight line, the resistance of the left and right driving wheels is roughly the same. The power output from the engine is first transferred to the differential housing so that the differential housing begins to turn. Next to transfer the power from the housing to the left and right half shaft, we can understand that the two sides of the half shaft gear in the "struggle" with each other, because the two sides of the wheel resistance is the same, so neither of the two can break each other, so the differential housing in the planetary gear with the housing to rotate at the same time will not produce rotation, two planetary gears with the two half shaft gear to rotate at the same speed, So the car can go straight!
Suppose the vehicle is now turning left and the left drive wheel travels a short distance, relatively speaking, it will produce more resistance. The differential housing is connected through the gear and the output shaft, and the speed of the differential housing is also unchanged when the speed of the drive shaft is unchanged, so the left half shaft gear will turn slower than the differential housing, which is equivalent to the planetary gear driving the left half shaft will be more difficult, then the planetary gear will produce autobiography, transferring more torque to the right half shaft gear. Due to the revolution of the planetary gear plus its own autobiography, the right half shaft gear will increase on the basis of the speed of the differential housing, so that the right wheel will turn faster than the left wheel, so that the vehicle can achieve a smooth turn.

Impact of differential on off-road performance:
Because the differential allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds, on muddy roads, when a wheel slips, the power is all consumed in the rapidly rotating skid wheel, and the other wheels will lose power. In popular words, the differential is used to make the vehicle turn when the wheel has a wheel speed difference, otherwise the vehicle will be difficult to turn, but the differential is helpful on the off-road road.
Therefore, in the four-wheel drive vehicle, it is also necessary to have a device to limit and prevent slipping, such as differential lock, limited slip differential, traction control system, etc.
